A dusty star-forming galaxy experiencing ram-pressure stripping in one of the most massive galaxy systems at cosmic noon
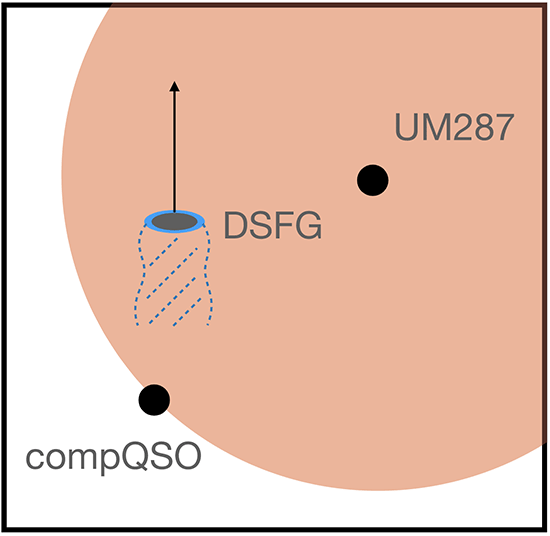
A dusty star-forming galaxy (DSFG) was discovered in the halo of a quasar pair system UM287, which also hosts an enormous Lyman-alpha nebula (ELAN). With observational evidence here is a proposed scenario of this system where over the past ∼100 Myr the DSFG has moved from south to north by ∼100 kpc in projected distance with a projected velocity of ∼1000 km/s; in the meantime, the DSFG experiences ram-pressure stripping and the stripped gas has been slowly entrained via shocks and gas mixing by the massive (∼10^12–10^13 Msun) hot halo of UM 287 with a virial radius of ∼150 kpc. The Slug-DSFG has also been experiencing strangulation, where the hot halo stops further accretion of cold gas so the gas reservoir has slowly drained out, therefore decreasing both the gas fraction and gas-to-dust ratios.